A Comprehensive Guide to Parts and Definitions
Almost every commercial establishment features escalators, remarkable inventions in their own right. Due to their complexity, only experts and highly skilled technicians can install, repair, and maintain these machines. While escalators may seem intricate, they become relatively straightforward to maintain and repair once the entire process is understood. However, mastering this procedure requires significant time and effort. For the average person, it’s helpful to know the essential components of an escalator. This is something you need to know while doing building management.
Summery’s Escalator Parts
The items include: brush, brush bracket, brake coil board, inverter, encoder main machine, cover, skirt panel, traffic light, handrail, friction wheel, handrail entrance assembly, step, step roller, step chain, step insert, step tread, comb, and front plate assembly.
Full description has given below:
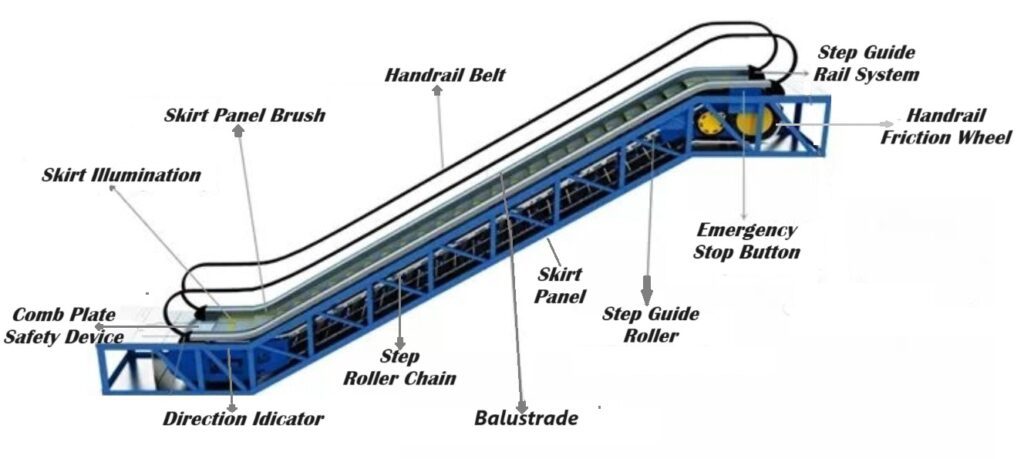
1) The Escalator Electronic Control System:
The Escalator Electronic Control System is a vital component that ensures the safe and efficient operation of an escalator. It consists of four main parts:
- Escalator PCB Board: This is the central circuit board that manages the escalator’s electrical functions, processing signals and controlling various systems.
- Escalator Brake: This safety device is responsible for stopping the escalator in case of an emergency or malfunction, ensuring passenger safety.
- Escalator Key Switch: This control switch allows authorized personnel to operate the escalator, enabling functions like starting, stopping, or changing the direction.
- Escalator Inspection Box: This is a control panel used during maintenance and inspection, allowing technicians to monitor and test the escalator’s performance safely.
2) The Supporting Structure and Track System:
- Truss: The steel frame that houses all the escalator’s machinery, divided into upper, middle, and lower sections.
- Truss Soffit: A steel plate installed underneath the truss.
- Truss Support Angle: An angled steel profile that connects the escalator to the building’s support beam.
- Middle Support(s): For tall escalators, additional supports are used to prevent bending.
- Track System: Guides the step wheels and chains along a circular path within the truss. It’s divided into upper, inclined, and lower tracks.
- Transition Radius: The curvature at the top and bottom of the track system.
3) Machinery and Passenger Interface:
- Machinery: The powerhouse of the escalator, encompassing all the motors, gearboxes, and drive components that keep it moving. This complex system ensures smooth and efficient operation.
- Machinery Spaces: Internal or external areas within the truss where the escalator’s machinery resides. These spaces are carefully designed to provide access for maintenance and inspection.
- Step/Pallet: The platform passengers stand on. Steps have treads and risers like stairs, while pallets are flat platforms used in moving walkways. Step design plays a crucial role in passenger comfort and safety
- Step/Pallet Width: Must comply with safety standards to ensure passenger comfort and prevent accidental missteps. The appropriate width allows for a secure and stable footing for all users.
- Step Trailing Roller: Two rollers are located beneath each step, guiding it along the track and ensuring smooth movement. To replace or get a price idea, you can click on the colored title.
4) Safety Features for Smooth Movement:
- Step Guide Roller: This roller fine-tunes the gap between the steps and the skirt panel, maintaining a safe distance to prevent objects from getting caught. Checkout here.
- Horizontal Steps: Flat sections at the landings allow passengers to enter and exit the escalator while maintaining balance. These level sections provide a safe transition zone.
- Comb: A toothed component at the landings that meshes with grooves on the steps, ensuring proper alignment and preventing steps from bunching up. This maintains a smooth and consistent ride.
- Comb Plate: The platform where the combs are mounted at the landings, providing a solid foundation for this crucial safety feature. To replace or get a price idea, you can click on the colored title.
- Comb Illumination: Lights are strategically placed on the skirt panels to illuminate the comb area during low-light conditions. This enhances passenger safety by improving visibility during entry and exit.
- Floor Plate: The platform surface at the landings, located next to the comb plate. It serves a dual purpose, providing a safe landing zone and sometimes concealing the machine room cover.
5) Handrail System for Stability:
- Handrail: A moving rubber belt passengers hold for support while riding the escalator.
- Handrail Friction Wheel: The profile that guides the handrail movement.
- Handrail Entrance/Exit: Where the handrail enters and exits the internal space.
- Handrail Inlet Guard/Return Guide: rubber and plastic components that guide the handrail smoothly.
- Handrail Guide Roller: Facilitates smooth handrail movement within the internal space.
- Handrail Pressure Belt: A set of rollers that press the handrail against the friction wheel, causing it to turn.
- g. Handrail Tension Device: Adjusts the tightness of the handrail. Escalator handrail belt drive tensioning is a process that ensures the handrail operates smoothly and safely. The tensioning system adjusts the belt that drives the handrail, maintaining the correct tension to prevent slippage or excessive wear.
6) Additional Features and Safety Measures:
- a. Balustrade Illumination: Optional lighting that enhances the balustrade’s aesthetics.
- b. Balustrade: The guardrail on both sides of the escalator for passenger safety and handrail support.
- c. Anti-Colliding/Sliding Devices: Installed at intersections or between parallel escalators to prevent passenger entrapment or falls.
- d. Access Restriction Device: Prevents unauthorized access to spaces between parallel escalators or those beside walls.
- e. Anti-Climbing Device: Deters climbing from outside the balustrade.
7) Skirt Panel :
- a. Skirt Panel: A vertical panel on both sides of the steps, maintaining a specific distance from them.
- b. Skirt Brush: Prevents objects from getting trapped between the skirt and steps.
- c. Skirt Illumination: Optional lighting to enhance the skirt panel’s appearance.
- d. Direction Indicator: Shows the escalator’s direction, especially in standby mode.
Conclusion: This comprehensive breakdown of an escalator’s parts equips you with valuable knowledge, particularly if you’re considering installing or modernizing one of your commercial property. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you’ll be better positioned to:
- Make informed choices: Grasping the function of each part allows you to discuss specific features and requirements with potential escalator suppliers. Prioritize safety: Knowledge of safety mechanisms like combs, demarcation cleats, and emergency brakes empowers you to prioritize passenger safety during the selection process. Ensure smooth operation: Understanding the handrail system, track
Read another article to learn about escalator safety.











Pingback: Escalator Pre-shipment Inspection (PSI) for the US Market
I like this blog very much, Its a rattling nice office to read and find info . “…when you have eliminated the impossible, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the truth.” by Conan Doyle.
Keep on writing, great job! https://yaninagames.com/